Last update images today Understanding The US Power Grid: A Comprehensive Map
Understanding the US Power Grid: A Comprehensive Map
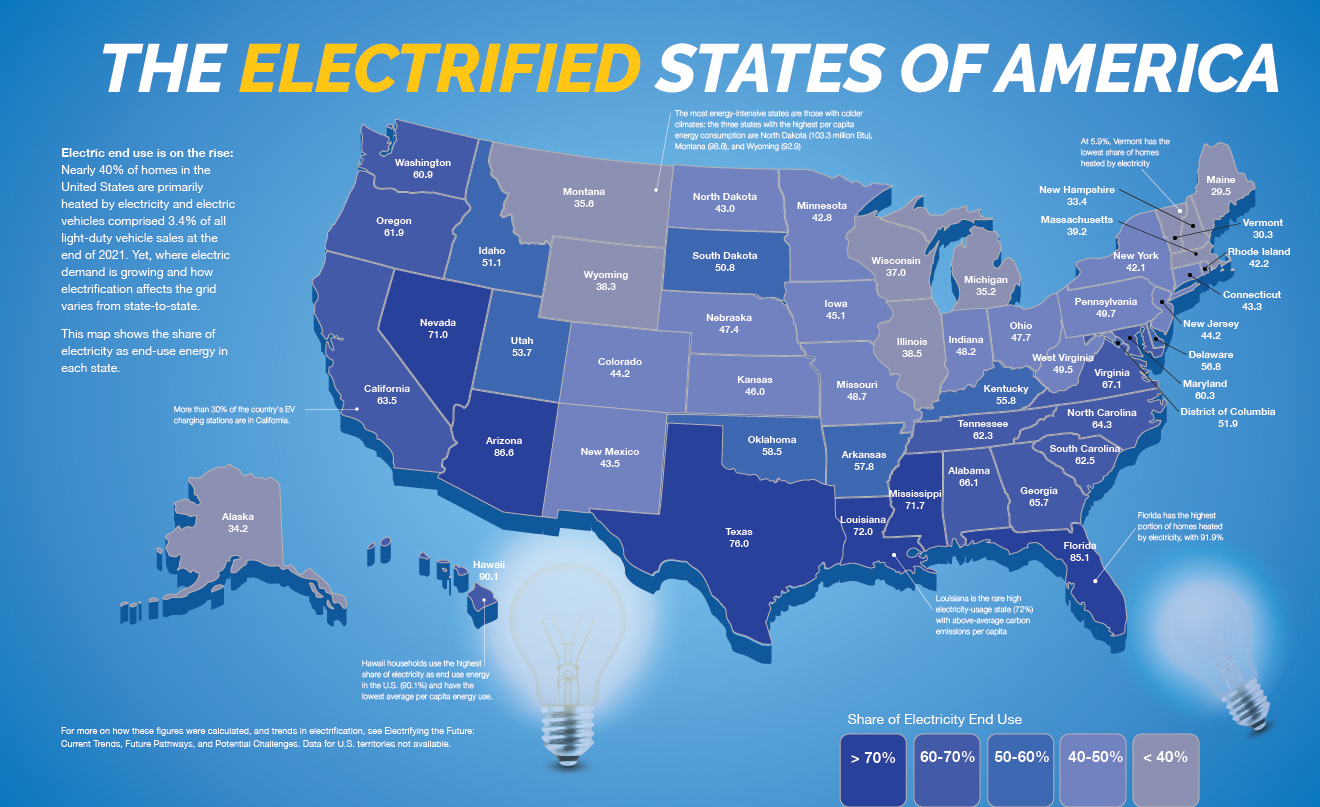
The stability and reliability of our electricity supply are often taken for granted, until the lights go out. Understanding the map of us power grids is crucial, especially given increasing weather events and evolving energy demands. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the US power grid, explores its complexities, and answers frequently asked questions, making it easy for anyone to grasp this essential infrastructure. This knowledge is power, especially in a world increasingly reliant on electricity.
1. The Basics: What is the Map of US Power Grids?
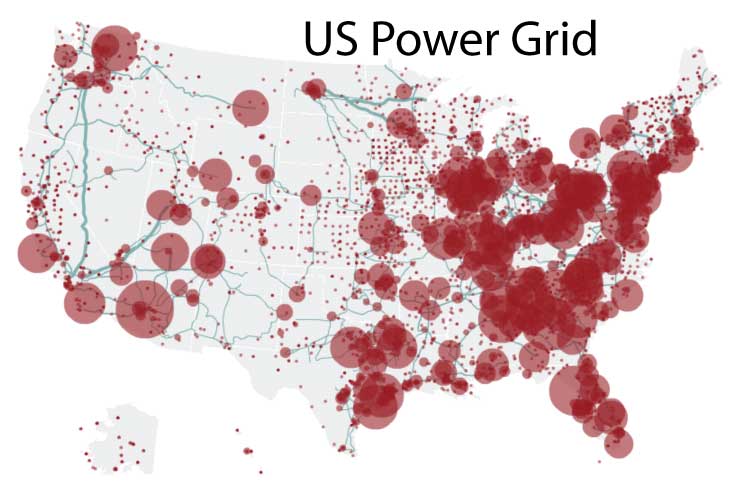
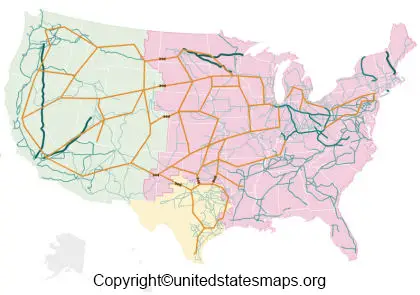
The map of us power grids isn't a single entity, but rather a vast, interconnected network of power plants, transmission lines, and distribution systems. These components work together to generate, transmit, and deliver electricity to homes and businesses across the United States. Think of it as a giant electrical highway system.
-
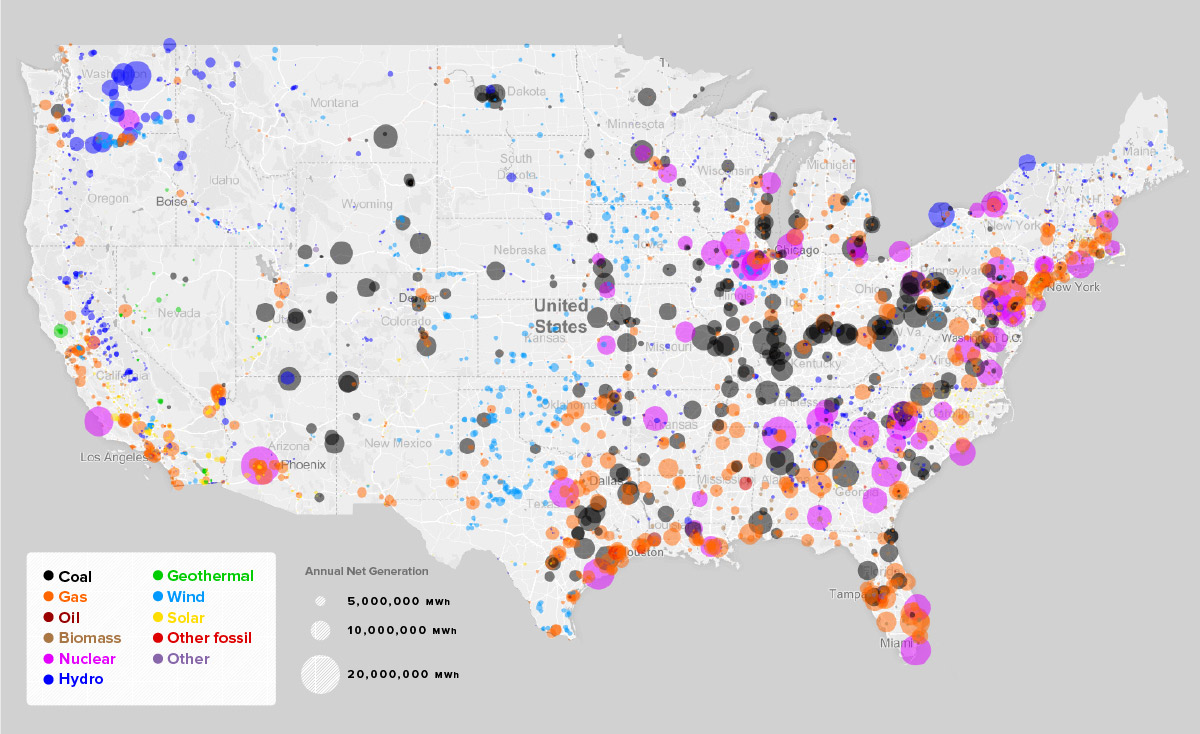
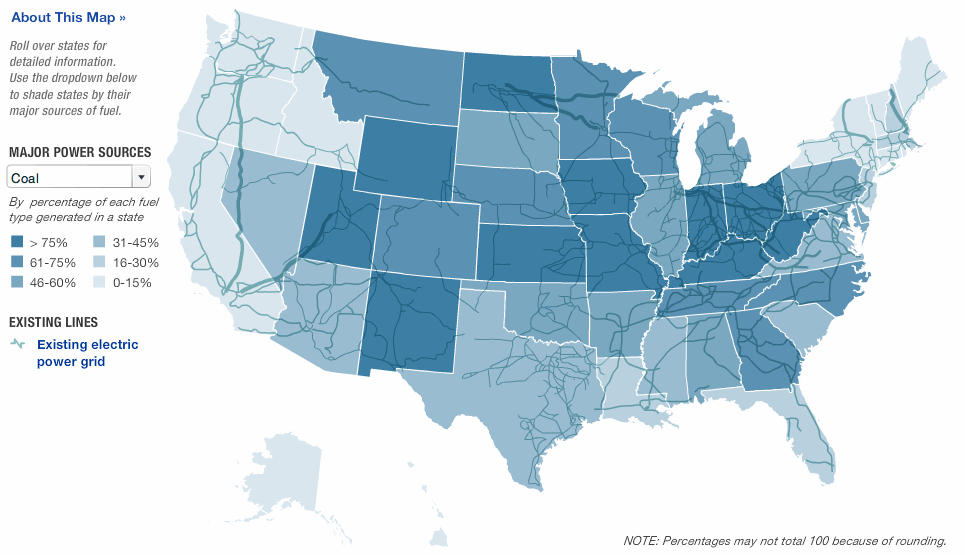
Generation: Power plants generate electricity using various sources, including fossil fuels (coal, natural gas), nuclear energy, and renewable sources (solar, wind, hydro).
-
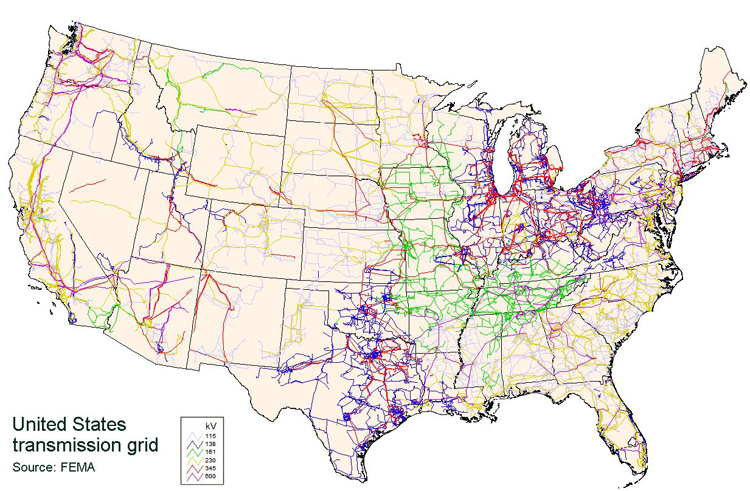
Transmission: High-voltage transmission lines carry electricity over long distances from power plants to substations.
-
Distribution: Substations lower the voltage of electricity before it's distributed to homes and businesses through local distribution lines.
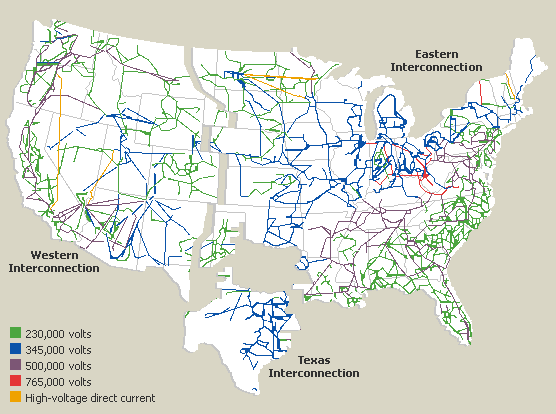
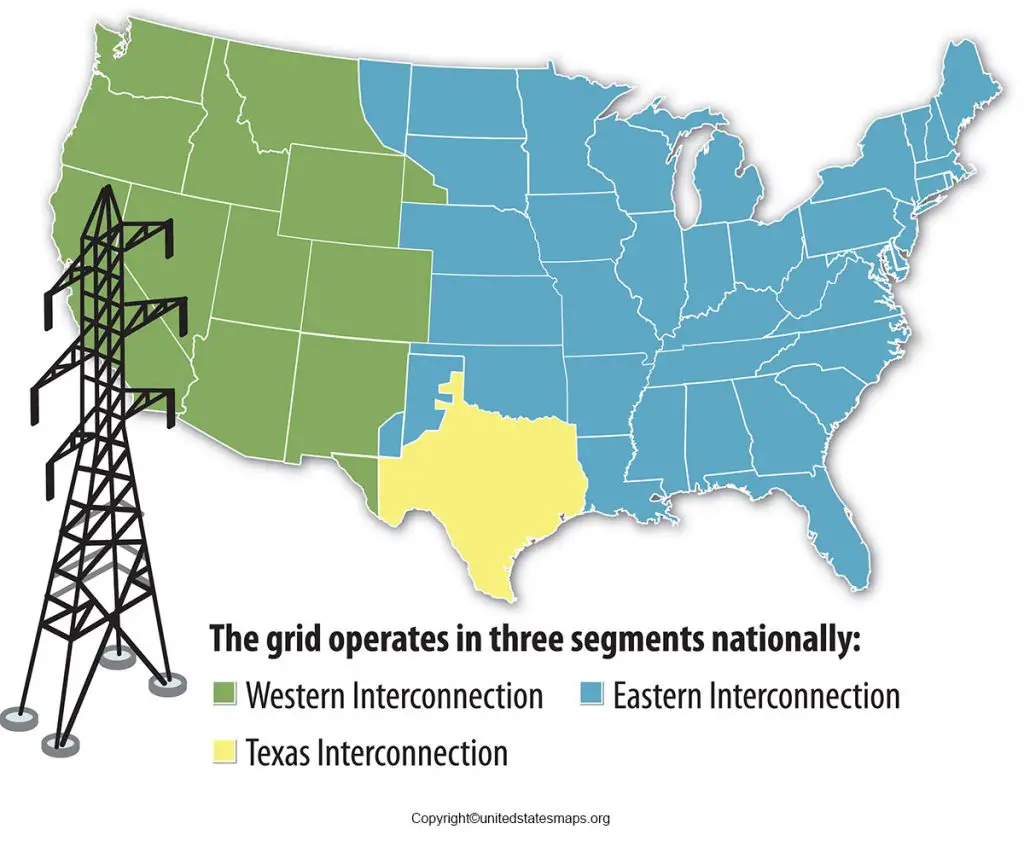
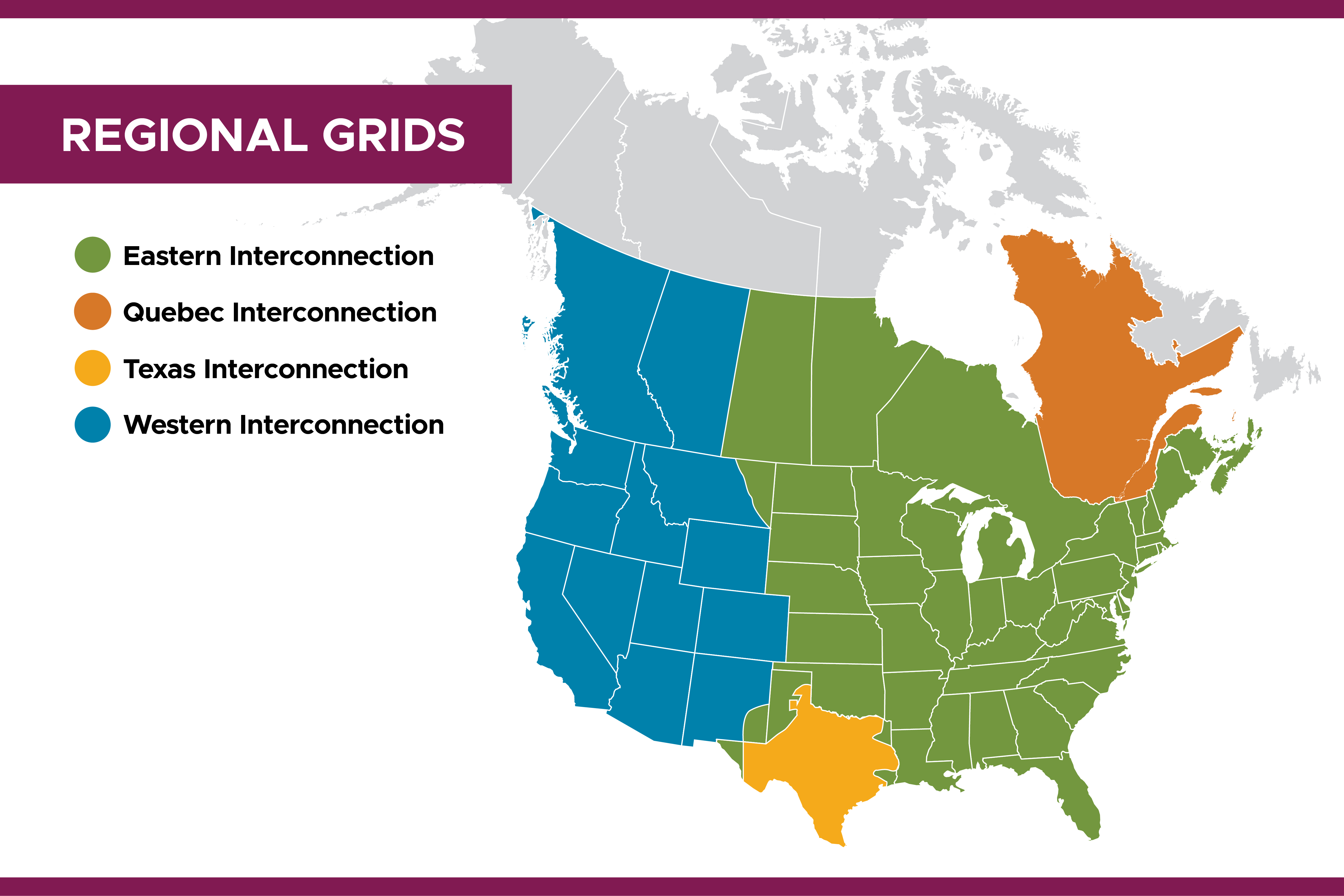
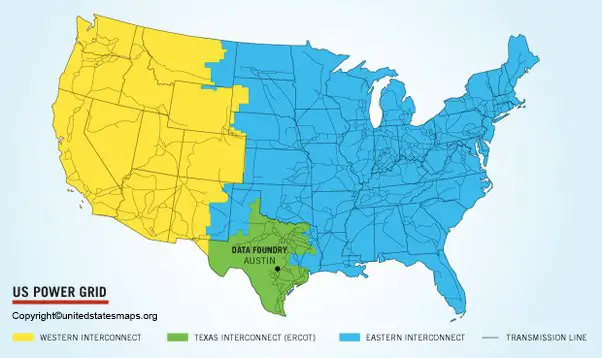
The map of us power grids can be visualized as three major interconnections: the Eastern Interconnection, the Western Interconnection, and the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). Each interconnection operates largely independently, although they are connected to a limited extent.
2. Decoding the Interconnections: Eastern, Western, and ERCOT. Map of US Power Grids.
The US power grid is not monolithic; it comprises three primary interconnected systems that function with considerable autonomy. Understanding these interconnections is critical to grasping the overall structure and operation of the map of us power grids.
-
Eastern Interconnection: The largest of the three, it covers the eastern half of the United States, stretching from the Atlantic coast to the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains. It also includes portions of eastern Canada. This vast area presents unique challenges in terms of coordination and reliability.
-
Western Interconnection: This covers the western portion of the United States, including the states west of the Rocky Mountains, as well as portions of western Canada and Baja California in Mexico. It operates on a different frequency than the Eastern Interconnection.
-
ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas): ERCOT manages the electrical grid in Texas. Unlike the other two interconnections, ERCOT operates largely independently and is not significantly connected to the rest of the US grid. This isolation has both advantages and disadvantages, as highlighted during severe weather events. The map of us power grids within Texas is managed solely by ERCOT.
3. Why is the Map of US Power Grids Important? Reliability and Resilience
Understanding the map of us power grids is essential for maintaining grid reliability and resilience. Reliability refers to the ability of the grid to consistently deliver electricity without interruption. Resilience refers to the grid's ability to withstand and recover from disruptions, such as severe weather events, cyberattacks, or equipment failures.
-
Preventing Blackouts: A well-understood grid map helps operators monitor grid conditions and take preventative measures to avoid blackouts.
-
Responding to Outages: Accurate grid information is crucial for quickly identifying the source of outages and restoring power to affected areas.
-
Planning for the Future: As the US transitions to a cleaner energy future, understanding the grid map is essential for planning the integration of renewable energy sources and upgrading infrastructure.
The map of us power grids serves as a crucial tool for emergency management, allowing authorities to quickly assess and respond to power outages during natural disasters or other emergencies.
4. The Future of the Map of US Power Grids: Modernization and Innovation
The map of us power grids is constantly evolving as new technologies and energy sources are integrated. Modernizing the grid is crucial for accommodating these changes and ensuring a reliable, resilient, and sustainable electricity supply.
-
Smart Grids: Smart grids use advanced sensors, communication technologies, and data analytics to improve grid monitoring, control, and efficiency.
-
Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources requires upgrades to transmission infrastructure and the development of new grid management techniques.
-
Energy Storage: Battery storage and other energy storage technologies can help stabilize the grid and improve the reliability of renewable energy sources.
The map of us power grids is becoming increasingly complex, requiring advanced software and analytical tools to manage and optimize its performance.
5. Common Questions and Answers About the Map of US Power Grids
Here are some frequently asked questions about the US power grid:
-
Q: Who owns the US power grid?
- A: The US power grid is owned and operated by a mix of public and private entities, including investor-owned utilities, public power utilities, and independent power producers.
-
Q: What is the difference between transmission and distribution lines?
- A: Transmission lines carry electricity over long distances at high voltages, while distribution lines deliver electricity to homes and businesses at lower voltages.
-
Q: How is the US power grid regulated?
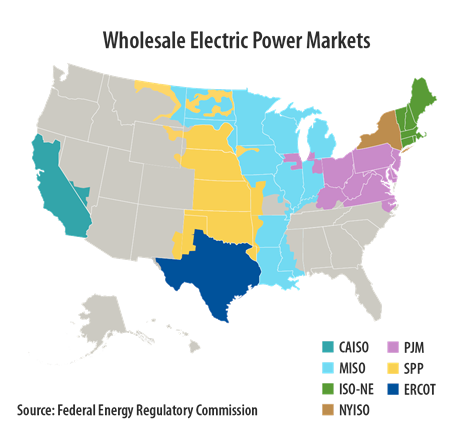
- A: The US power grid is regulated by both federal and state agencies. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, while state public utility commissions regulate the distribution of electricity within their states.
-
Q: What are the biggest challenges facing the US power grid?
- A: The biggest challenges facing the US power grid include aging infrastructure, increasing demand for electricity, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the threat of cyberattacks.
-
Q: How can I find a map of my local power grid?
- A: Contact your local utility company. Many provide online resources, including maps of their service areas and planned outages. Access the map of us power grids information specific to your region.
Keywords: Map of US Power Grids, US Power Grid, Power Grid, Electricity, Energy, Grid Reliability, Grid Resilience, Smart Grid, Renewable Energy, ERCOT, Eastern Interconnection, Western Interconnection, Power Plants, Transmission Lines, Distribution Lines, Blackout, Power Outage.
Summary: What is the map of US power grids and why is it important? The US power grid is a complex network for electricity delivery, divided into three main interconnections (Eastern, Western, ERCOT). Understanding this map is vital for reliability, resilience, and future modernization.
The Electrified States Of America American Public Power Association PPM September October 2022 Electrification Map Graphic Full Power Grid Going Out 2024 Annis Brianne Us Electric Grid Energy Transition Index FacebookJumbo Us Map In 2025 Brear Peggie 90Electricity Map Picture1 Power Grid Map Of US United States Maps Power Grid Map Of Us 1024x841 Map Of Us Electrical Grid Map Screen Shot 2020 04 19 At 18.25.39 This Interactive Map Shows US Electricity Usage In Real Time World Large M4AQ7zWW7VJz0DiW95gTZDnVQdCVAkezQ7leXtIrB4M.PNGThis Map Shows Every Power Plant In The United States Us Power Plants Map
U S Electricity Grid Markets US EPA Gpp Wholesale Electric Power Markets 0 Power Grid Map Of US United States Maps Us Power Grid Map 1024x607 Interactive Map Visualizing The U S Electric Grid InfrastructureUSA Screen Shot 2011 05 24 At 41047 Pm NPR Maps Out The United States Vein Y Power Grid 49 OFF Us Electric Grid Energy Transition Index MediumSquareAt3X Map Of United States Of America Electricity Grid United States Of USA Grid Macrogrid Study Big Value In Connecting America S Eastern And Western 5KW6
U S Grid Regions US EPA Egrid Subregions Map Power Grid Fundamentals And Electricity Pricing EnergyCAP 1 EBook PowerGrid USGrid2 The U S Electricity System In 15 Maps Sparklibrary Florida Power The U S Electricity System In 15 Maps Sparklibrary Florida Power Grid Map Map Of Us Electric Grid Map Electrical Grid Distribution In The US Department Of Energy Graphics Courtesy Of Interactive Map Visualizing The U S Electric Grid InfrastructureUSA Screen Shot 2011 05 24 At 41016 Pm US Power Grid Map Power Grid Map Of US Printable Power Grid Map Of Usa Navigating The Energy Grid A Deep Dive Into The US Electrical Grid Map Us Power Grid Map
Proposed HVDC Macrogrid To Transmit Low Cost Renewable Power Pv VCE Clean Economy 2050 And UG HVDC Overlay Map 1200x750 Visualized How The Power Grid Works SHAREABLE NPUC US Power Generation 08022023 01 1000x600 Map Of The Us Power Grid 2024 Schedule 1 Screen Shot 2018 06 17 At 12.55.41 PM US Power Grid Map Power Grid Map Of US Printable Usa Power Grid Map U S Electric System Is Made Up Of Interconnections And Balancing Main PMUs In North American Power Grids Source From The ArticleT D World PMUs In North American Power Grids Source From The ArticleT D World Grid Innovation
Electric Transmission And Distribution Network GEOG 469 Energy UnitedStatesPowerGrid 750px Simulating The Role Of Grid Forming Inverters In The Future Electric Grid EED 1616 ILLUS US CanadaGridMap V1