Last update images today Asexual Plant Images: Trending Now
Asexual Plant Images: Trending Now!
Introduction: Unveiling Nature's Cloning Power
Have you ever wondered how a single plant can seemingly multiply without seeds? The secret lies in asexual reproduction, and this week, interest in "asexual plant images" is blossoming! This article explores the fascinating world of asexual plant reproduction, offering insights, stunning visuals, and answering your burning questions. Discover the diverse methods plants use to clone themselves, their benefits, and how you can use this knowledge in your own garden.
Target Audience: Gardeners of all levels, botany enthusiasts, students, teachers, nature photographers, anyone curious about plant reproduction.
Understanding Asexual Plant Images: What is Asexual Reproduction?
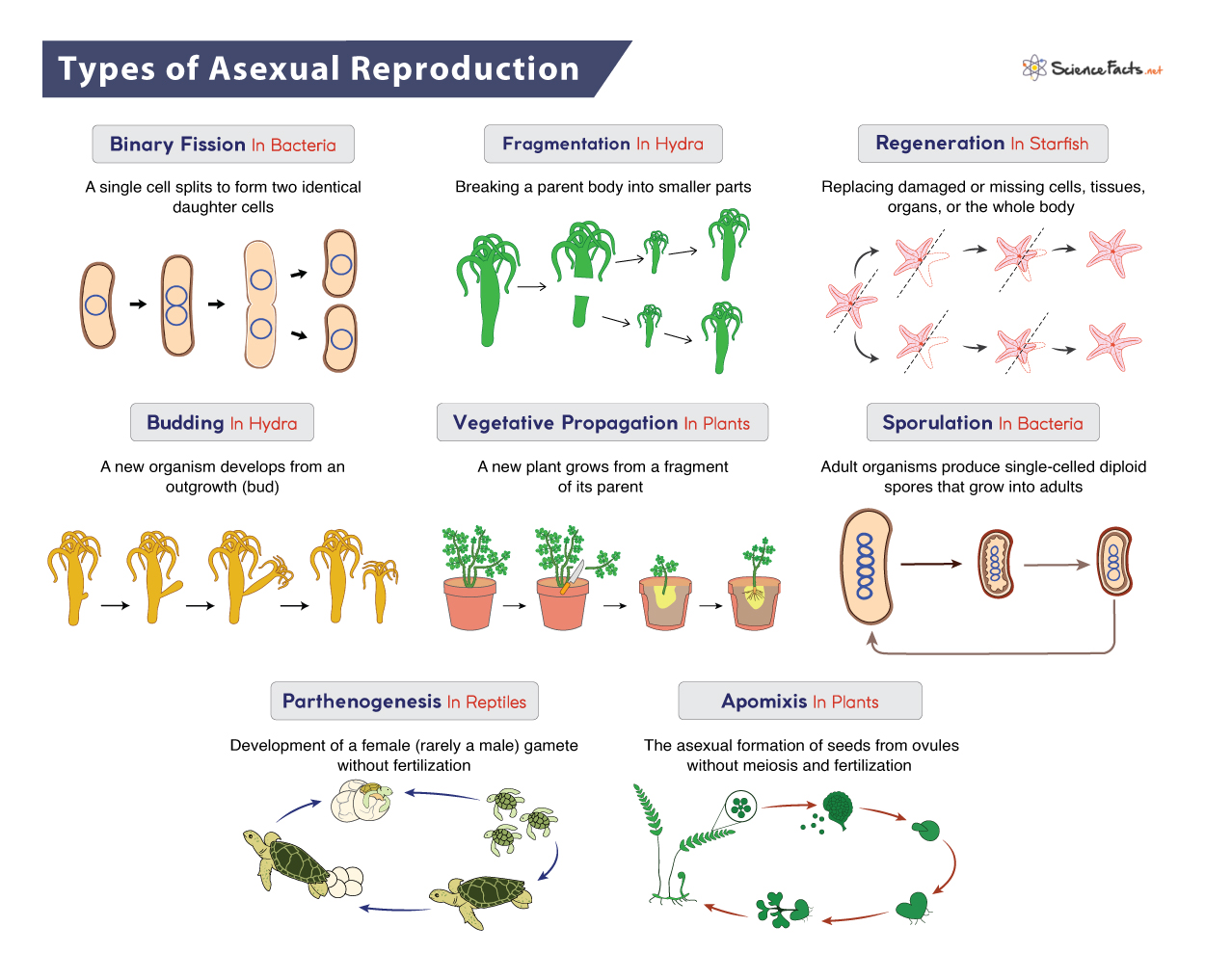
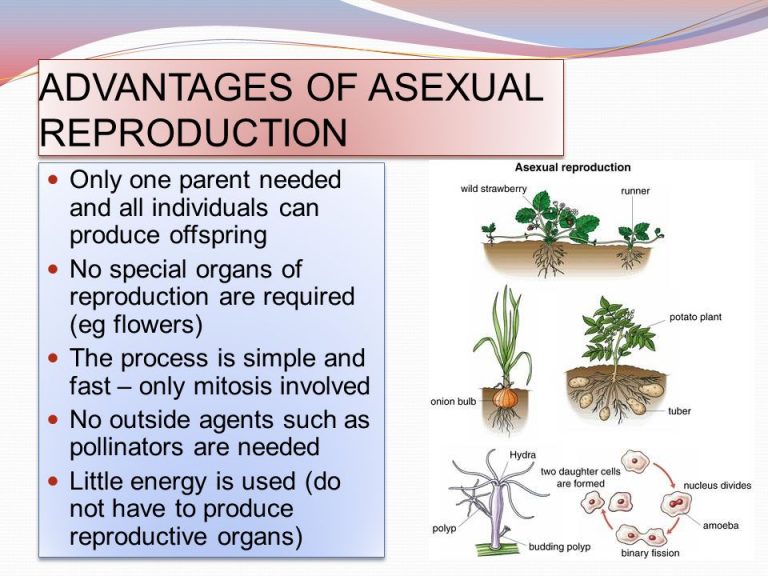
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that doesn't involve the fusion of gametes (sex cells). Instead, a new plant grows from a part of the parent plant, resulting in a genetically identical offspring, essentially a clone. The appeal of "asexual plant images" stems from their depiction of nature's ingenuity in creating exact copies of successful plants.
- No seeds needed!
- Offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
- Faster reproduction in some cases.
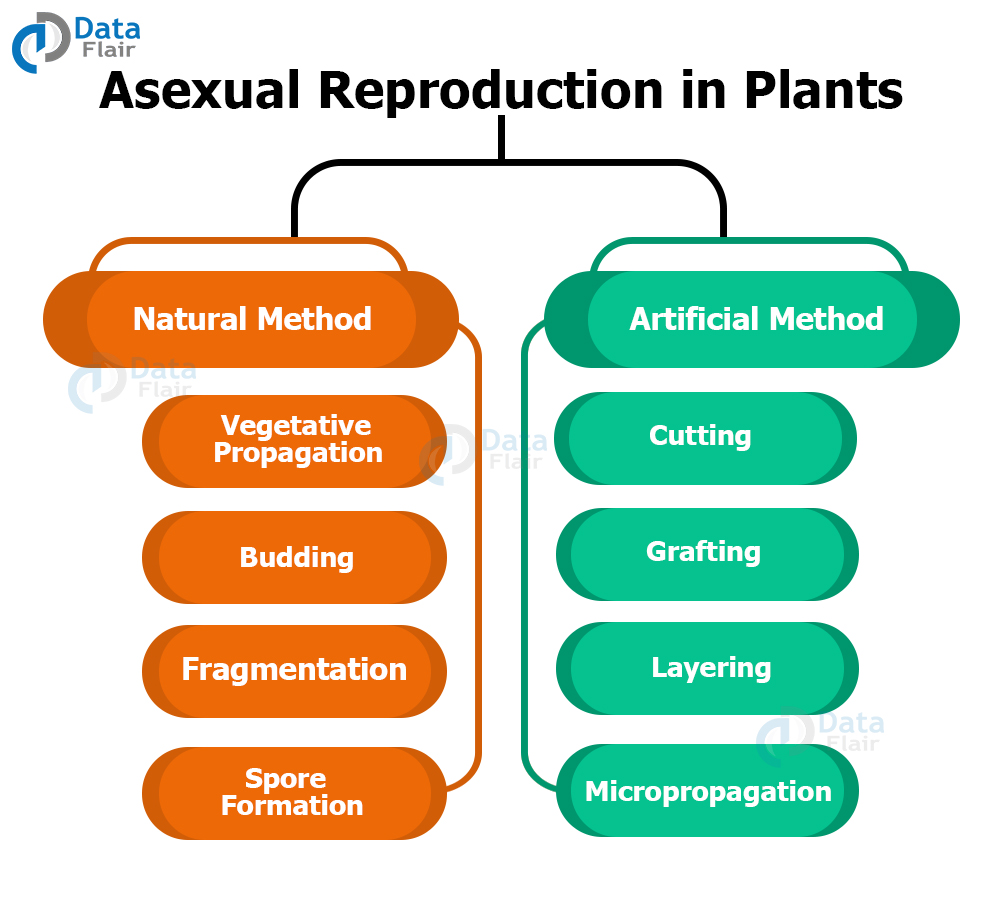
Exploring Asexual Plant Images: Different Methods of Asexual Reproduction
Plants have evolved various ingenious strategies for asexual reproduction, each offering unique "asexual plant images". Here are some of the most common methods:
-
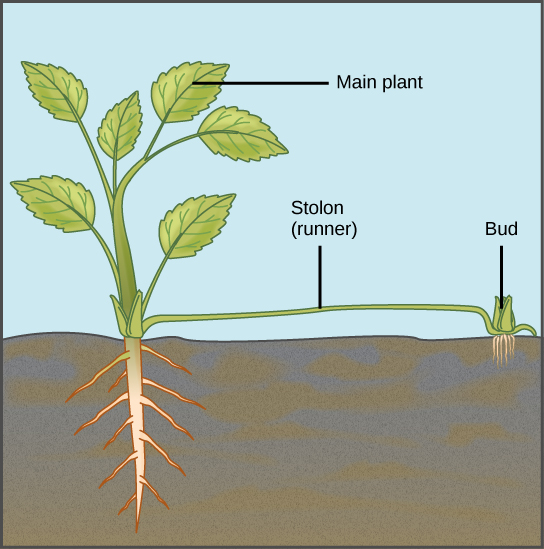
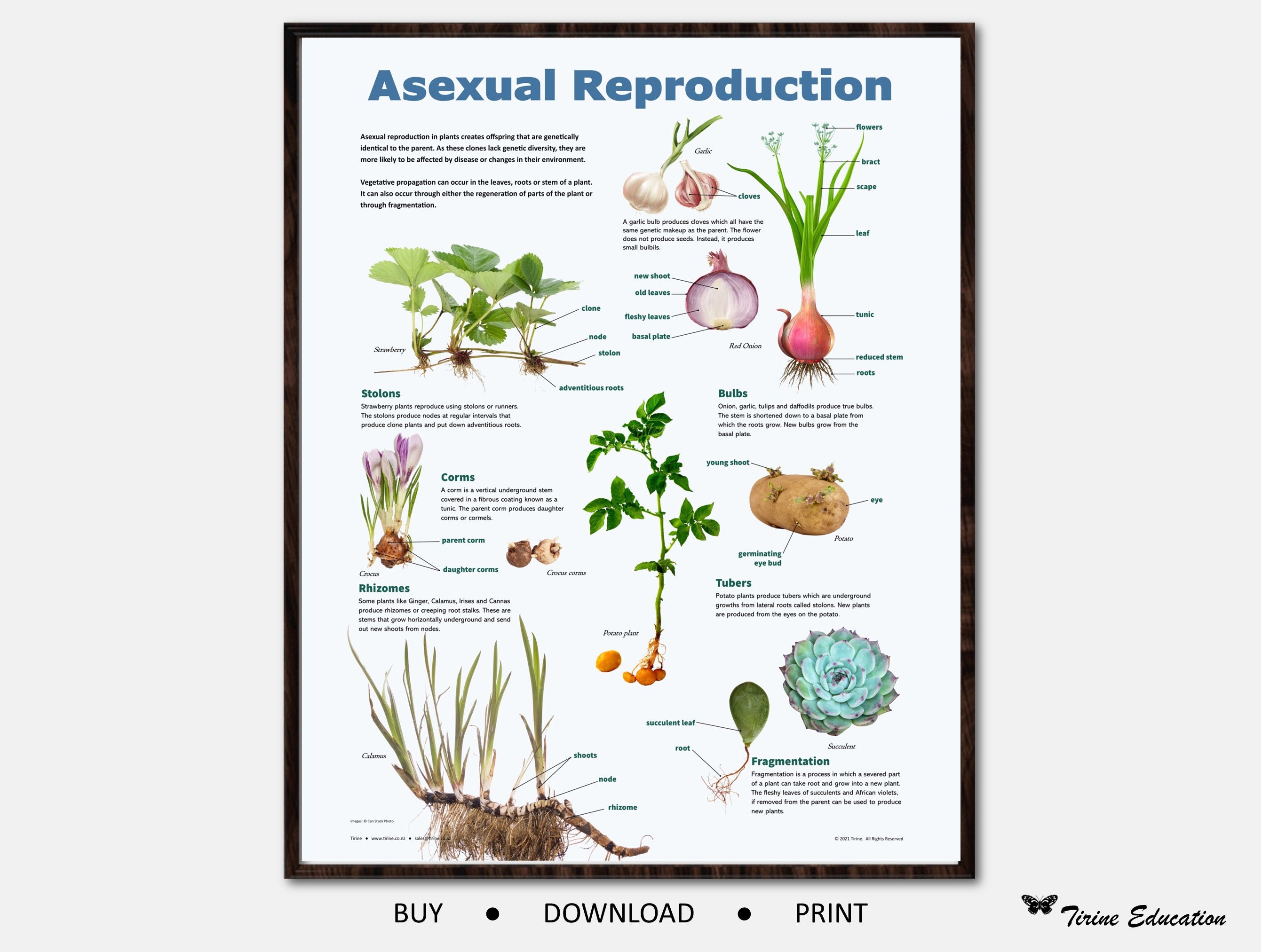
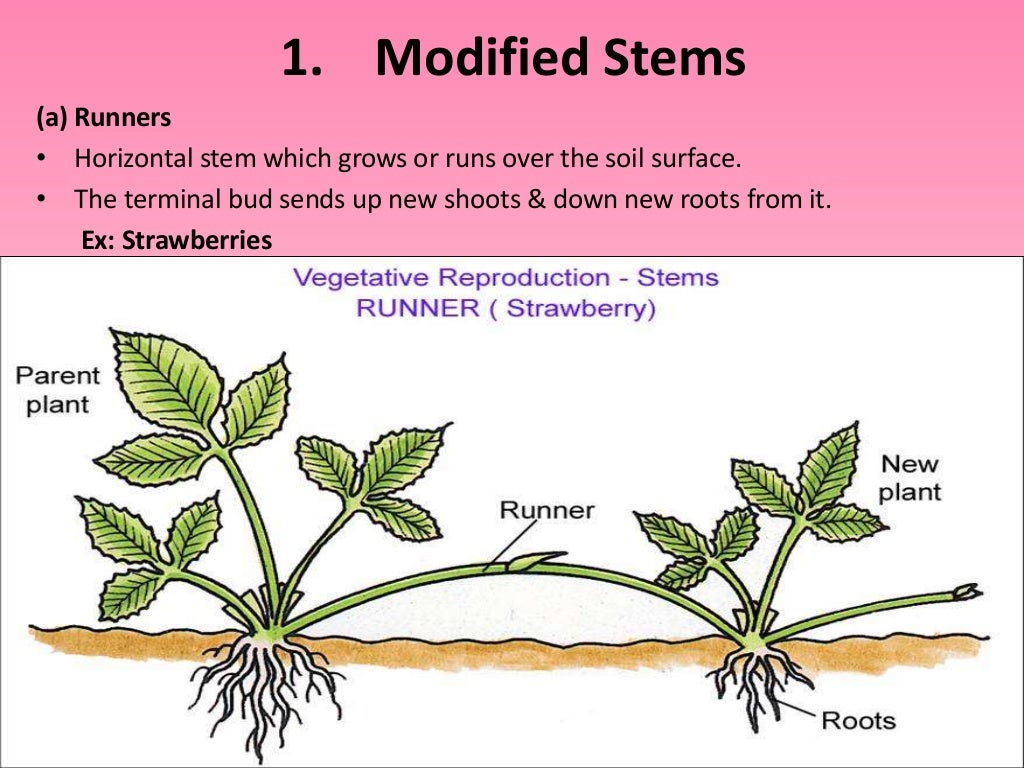
Runners (Stolons): Strawberry plants are a classic example. They send out horizontal stems called runners or stolons, which grow along the ground. At nodes along the runner, new roots and shoots develop, forming a new plant. Images showcasing strawberry runners are popular "asexual plant images."
-
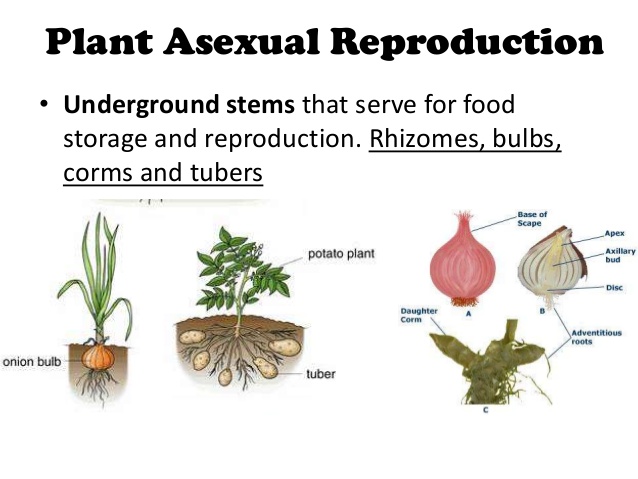
Rhizomes: These are underground stems that can grow horizontally and send up new shoots and roots at intervals. Ginger and bamboo are well-known examples. Search for "asexual plant images rhizomes" to witness their underground network.
-
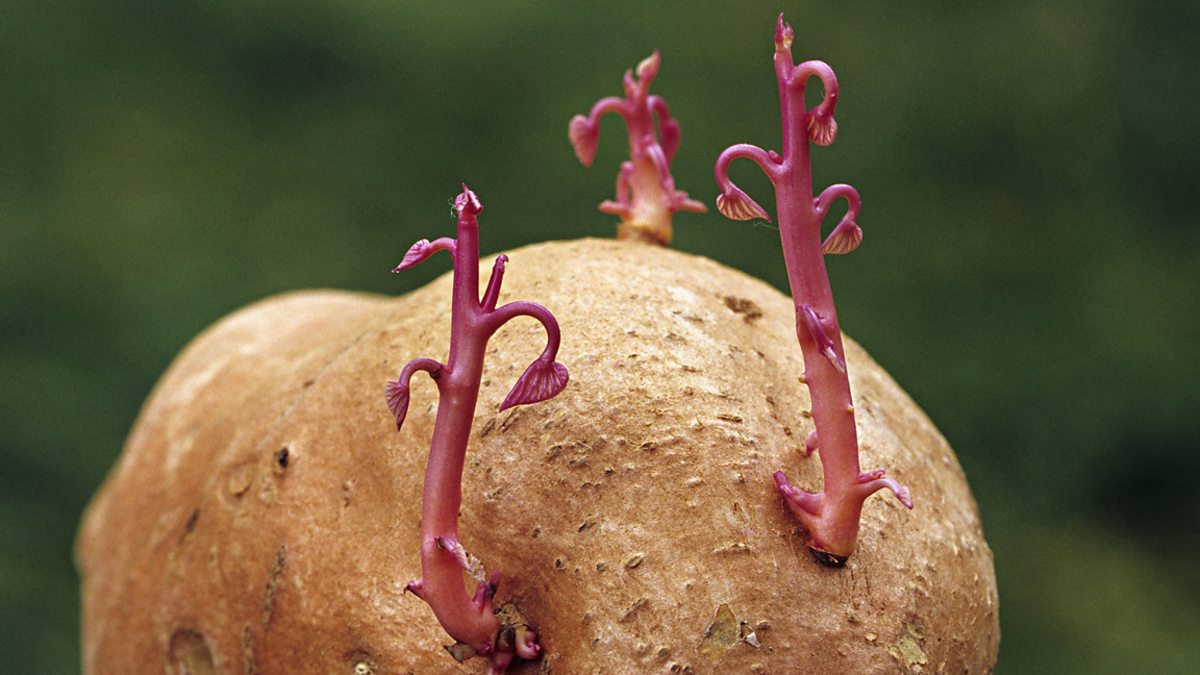
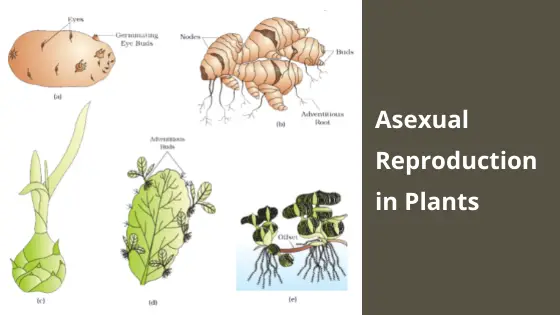
Tubers: Potatoes are modified underground stems called tubers that store food. Each "eye" on a potato can sprout into a new plant. A great example to search for "asexual plant images."
-
Bulbs: Onions, garlic, and tulips reproduce using bulbs. Bulbs are underground stems with fleshy scales that store food. New bulbs can develop from the parent bulb, leading to clonal growth. Search "asexual plant images bulbs" to understand how they cluster.
-
Corms: Similar to bulbs, corms are solid, swollen underground stems. Gladiolus and crocus reproduce through corms. "Asexual plant images corms" can reveal the difference between bulbs and corms.
-
Plantlets: Some plants, like Kalanchoe (Mother of Thousands), produce tiny plantlets along their leaf margins. These plantlets drop off and root, creating new individuals. "Asexual plant images plantlets" are especially striking.
-
Fragmentation: This is the separation of a piece of the parent plant, which then develops into a new individual. Many succulents and cacti can be propagated through stem or leaf cuttings. The images of succulents rooting are popular.
-
Grafting: In this technique, a stem or bud from one plant (the scion) is joined to the rootstock of another. This allows for the propagation of desirable traits, such as specific fruit varieties. "Asexual plant images grafting" highlights this horticultural practice.
-
Tissue Culture (Micropropagation): This advanced technique involves growing plant cells or tissues in a sterile nutrient medium to produce a large number of identical plants. This is common in commercial nurseries. Searching for "asexual plant images tissue culture" will show the technology involved.
Why are Asexual Plant Images Trending? The Benefits of Asexual Reproduction
The renewed interest in "asexual plant images" reflects a growing awareness of the advantages of this reproductive strategy:
-
Speed: Asexual reproduction can be much faster than sexual reproduction (from seeds), allowing for quicker propagation of desired plants. This is why you see so many "asexual plant images" related to gardening tips.
-
Consistency: Asexual reproduction ensures that the offspring are genetically identical to the parent, preserving desirable traits. If you have a prize-winning rose bush, asexual reproduction is the way to go!
-
Adaptation: Asexual reproduction can be advantageous in stable environments where the parent plant is well-adapted.
-
Bypassing Seed Dormancy: Some seeds have long dormancy periods. Asexual reproduction bypasses this issue, allowing for quicker establishment.
Seeing Asexual Plant Images in Action: Examples in Your Own Backyard
Many common garden plants reproduce asexually. Keep an eye out for these examples, and capture your own "asexual plant images":
- Strawberries: Look for runners extending from established plants.
- Mint: Be careful! Mint spreads rapidly through rhizomes.
- Potatoes: Watch for new shoots emerging from stored potatoes.
- Daylilies: Divide clumps of daylilies to propagate them.
Using Asexual Plant Images for Inspiration: Propagating Plants Asexually
The beauty of "asexual plant images" often inspires people to try propagating their own plants. Here are a few tips:
- Cuttings: Take stem cuttings from plants like rosemary, lavender, and geraniums. Dip the cut end in rooting hormone and plant in well-draining soil.
- Division: Divide clumps of plants like hostas, daylilies, and irises.
- Layering: Bend a stem down to the ground and bury a section of it. Once roots form, you can cut the stem from the parent plant.
The Future of Asexual Plant Images: Technology and Beyond
"Asexual plant images" are not just aesthetically pleasing; they represent a powerful biological process with significant implications for agriculture and horticulture. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more sophisticated methods of asexual reproduction, such as advanced tissue culture techniques and genetic engineering to enhance desirable traits.
Conclusion: Appreciating Nature's Cloning Mastery
The world of asexual plant reproduction is fascinating and diverse. "Asexual plant images" offer a glimpse into the amazing strategies plants have evolved to propagate themselves. By understanding these methods, we can become better gardeners and appreciate the ingenuity of the natural world.
Keywords: asexual reproduction, plant propagation, runners, rhizomes, tubers, bulbs, corms, plantlets, fragmentation, grafting, tissue culture, "asexual plant images", gardening, horticulture, clone, genetic copy, plant cutting, plant division.
Summary Question and Answer:
Q: What is asexual reproduction in plants?
A: Asexual reproduction is a process where a new plant grows from a part of the parent plant without the fusion of gametes (sex cells), resulting in a genetically identical offspring.
Q: Why are "asexual plant images" trending?
A: Because they showcase the fascinating diversity and effectiveness of asexual reproduction in plants, highlighting its benefits like speed, consistency, and bypassing seed dormancy.
Asexual Reproduction In Plants Plant Reproduction The Biology AsexualReproductionTPT Asexual Reproduction In Plants Propagating And Growing Plants P01cgxnq Asexual Reproduction In Plants Diagram A66f3b63084451ceac0ec946da497024 Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Reproduction Model Asexual Maxresdefault Asexual Plant Propagation YouTube Maxresdefault 32 12 Asexual Reproduction Natural And Artificial Methods Of Asexual Figure 32 03 02
Asexual Reproduction In Plants Ks2 Worksheets Asexual Reproduction In Plants 1 1024 Advantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants FarmPally Com Advantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants By Farmpally.com 768x576 Asexual Plant Reproduction Biology YouTube Maxresdefault Asexual Reproduction In Plants Diagram Slide 11 1024 Types Of Asexual Plants 12 Examples And Images UpHomely Plant Texture Structure Leaves Nature Coleus Blumei Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science 3eaeb45af08e5237a6f15a466893b561 Asexual Reproduction Science Education Asexual Reproduction In Plants Poster Science Biology Middle School Il 1080xN.6192628648 G6bb Asexual Plants Il Fullxfull.4878833434 E1rz
Do Flowers Reproduce Plants At Darryl Graves Blog Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Reproduction Ppt Download Examples Include Spider Plant Asexual Plants Image Asset Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Reproduction In The Plants 99 Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants How Does It Work Medical Reproduccin Sexual Y Asexual En Las Plantas Cmo Funciona.webpPlant Asexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids YouTube Maxresdefault Reproduction In Plants Sexual Reproduction And Asexual Reproduction Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Plant Propagation Maxresdefault
Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Reproduction In Plants 6 1024 Reproduction In Plants Sexual Reproduction And Asexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction In Plants Asexual Reproduction In Plants Diagram Buddinginhydra Different Forms Of Asexual Plant Reproduction Explained Britannica Plants Variety Ways Differentiate The 3 Types Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants At Timothy Maxresdefault 32 11 Asexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology Figure 32 03 01.jpeAsexual Reproduction In Plants Definition Methods Biology Notes Online Asex.webpWhat Is Asexual Reproduction In Plants And Animals At Nate Collins Blog Types Of Asexual Reproduction
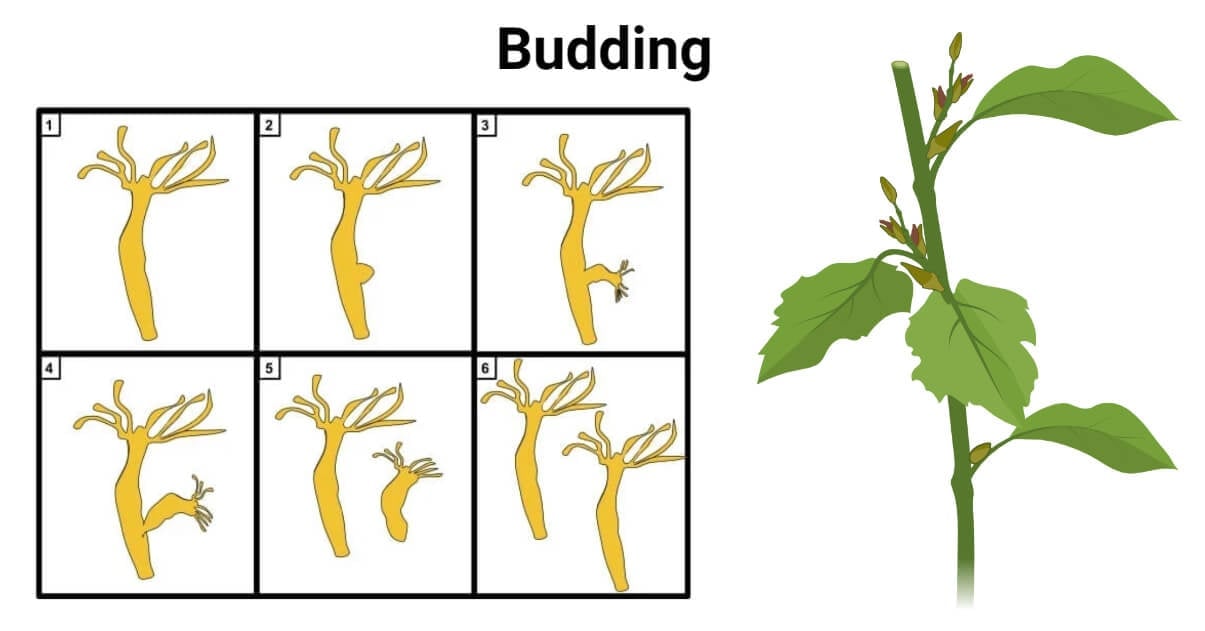
Budding Asexual Reproduction In Plants Budding 10 Asexual Plants And Their Characteristics Science 2025 Nutricin Auttrofa Caractersticas Etapas Tipos Ejemplos 4.webpAsexual Reproduction In Plants And Animals Definition With Examples Asexual Reproduction In Plants And Animals 12 Orig